Explain the Respiratory Assessment Differences Between Pe and Pneumonia
Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. If risk assessment indicates the need for respiratory protection drivers medical or security staff and others who are transporting patients with suspected or confirmed infectious TB disease in an enclosed vehicle should consider wearing an N95 disposable respirator.

Aspiration Pneumonia A Renewed Perspective And Practical Approach Respiratory Medicine
No differences were found in effectiveness between the two agents.

. 20 Full PDFs related to this paper. Students will reinforce their acquired knowledge by creating an assessment on metabolic vs. Results The rates of all infection outcomes were highest in the cloth mask arm with the rate of ILI statistically significantly higher in the cloth mask arm relative risk RR1300 95 CI 169 to 10007 compared with the medical mask arm.
There were no significant adverse events and no patient failed to improve with NIV. Racialethnic minorities are at higher risk for severe COVID-19. In another report the addition of infused dexmedetomidine to a standard protocol of as needed bolus intravenous midazolam and fentanyl given according to a sedation protocol failed to show benefit but sedation goals were.
Respiratory mucosal immunization with a next-generation adenoviral-vectored trivalent COVID-19 vaccine expressing spike nucleocapsid and RdRp antigens induces all-around protective mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 via induction of systemic and local antibodies lung-tissue-resident memory T cells and trained alveolar macrophages. This may be related to social determinants that lead to chronic inflammatory states. The two viruses share characteristics such as morphology and replication strategy with.
The differences between the two. Main outcome measure Clinical respiratory illness CRI influenza-like illness ILI and laboratory-confirmed respiratory virus infection. In February 2020 the World Health Organization designated coronavirus disease 2019 COVID-19 as the name of the human disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 SARS-CoV-2 which was previously known as 2019-nCoV 2019 novel coronavirus.
The under-five mortality rate which is referred to as the child mortality rate is also an important statistic considering the infant mortality rate focuses only on. This was a secondary analysis of a retrospective. Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
2 Viral pneumonia is the most frequent serious clinical manifestation of COVID. Download Full PDF Package. The aims of the study were to determine if there are racialethnic disparities with inflammatory markers and association of methylprednisolone to in hospital survival.
Physiology PreTest Self-Assessment and Review 14th Ed. Whenever feasible sampling of lower respiratory tract LRT secretions ie obtaining bronchoalveolar lavage BAL fluid or endotracheal aspirate ETA samples is crucial to provide detection of organisms coupled with assessment of their bacterial loads in COVID-19 patients who develop VAP or non-VAP hospital-acquired pneumonia HAP during the ICU stay. Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1.
Respiratory acidosis for other students studying the same topic. A short summary of this paper. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial virus BRSV and Bovine Parainfluenza 3 virus BPIV3 are closely related viruses involved in and both important pathogens within bovine respiratory disease BRD a major cause of morbidity with economic losses in cattle populations around the world.
However differences in virulence factors eg H1N1 influenza coexisting conditions eg pneumococcal pneumonia after splenectomy and environmental exposures alcohol use or active smoking. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate IMR which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. A respiratory-protection program including training education and fit-testing in the correctional.
2 7 Focused Assessments Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care
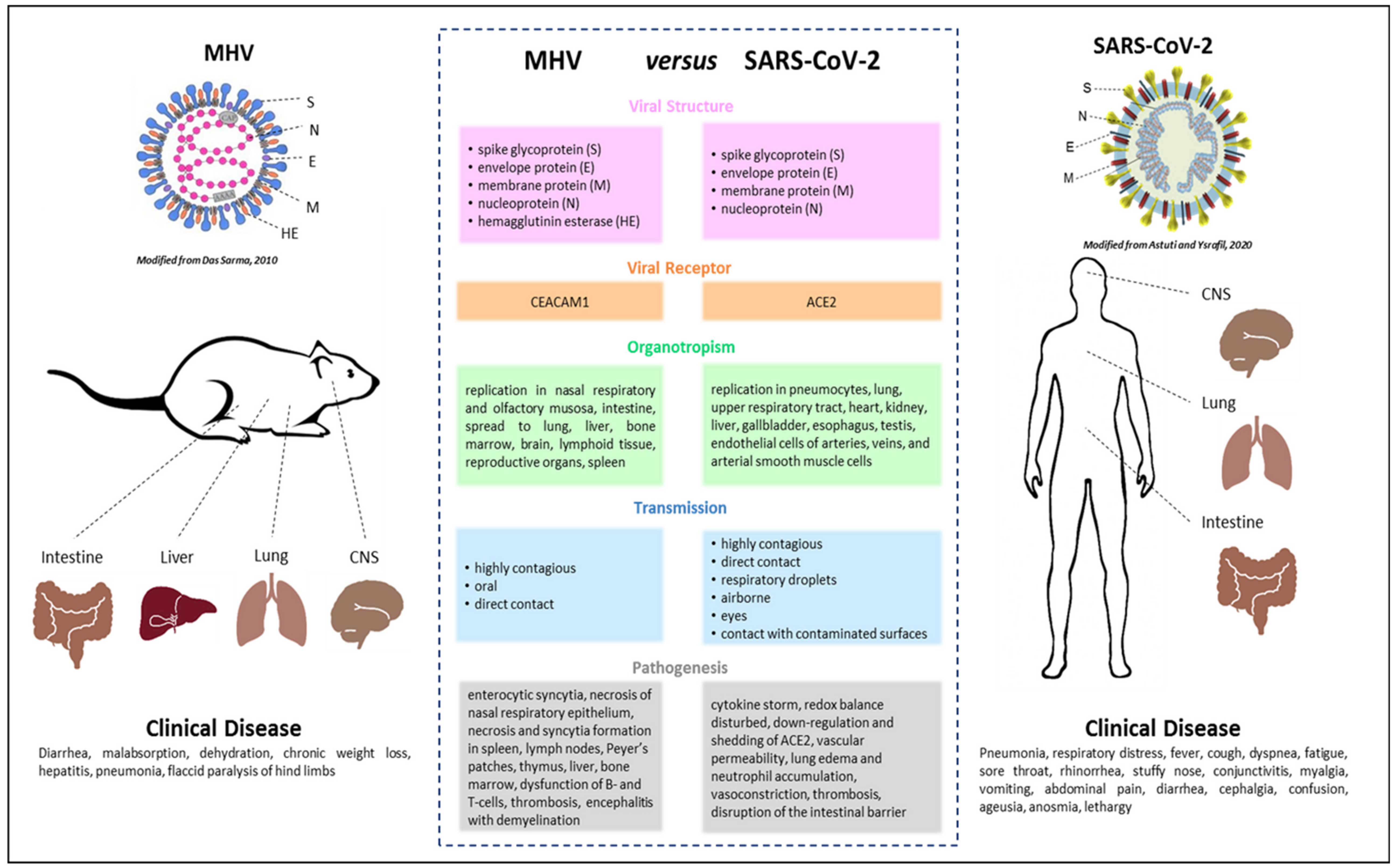
Viruses Free Full Text Of Mice And Men The Coronavirus Mhv And Mouse Models As A Translational Approach To Understand Sars Cov 2 Html

Assessment Of Pulmonary Arterial Circulation 3 Months After Hospitalization For Sars Cov 2 Pneumonia Dual Energy Ct Dect Angiographic Study In 55 Patients Eclinicalmedicine

Non Invasive Diagnosis Of Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Incidence Of Acute Pulmonary Embolism In Covid 19 Patients Systematic Review And Meta Analysis European Journal Of Internal Medicine
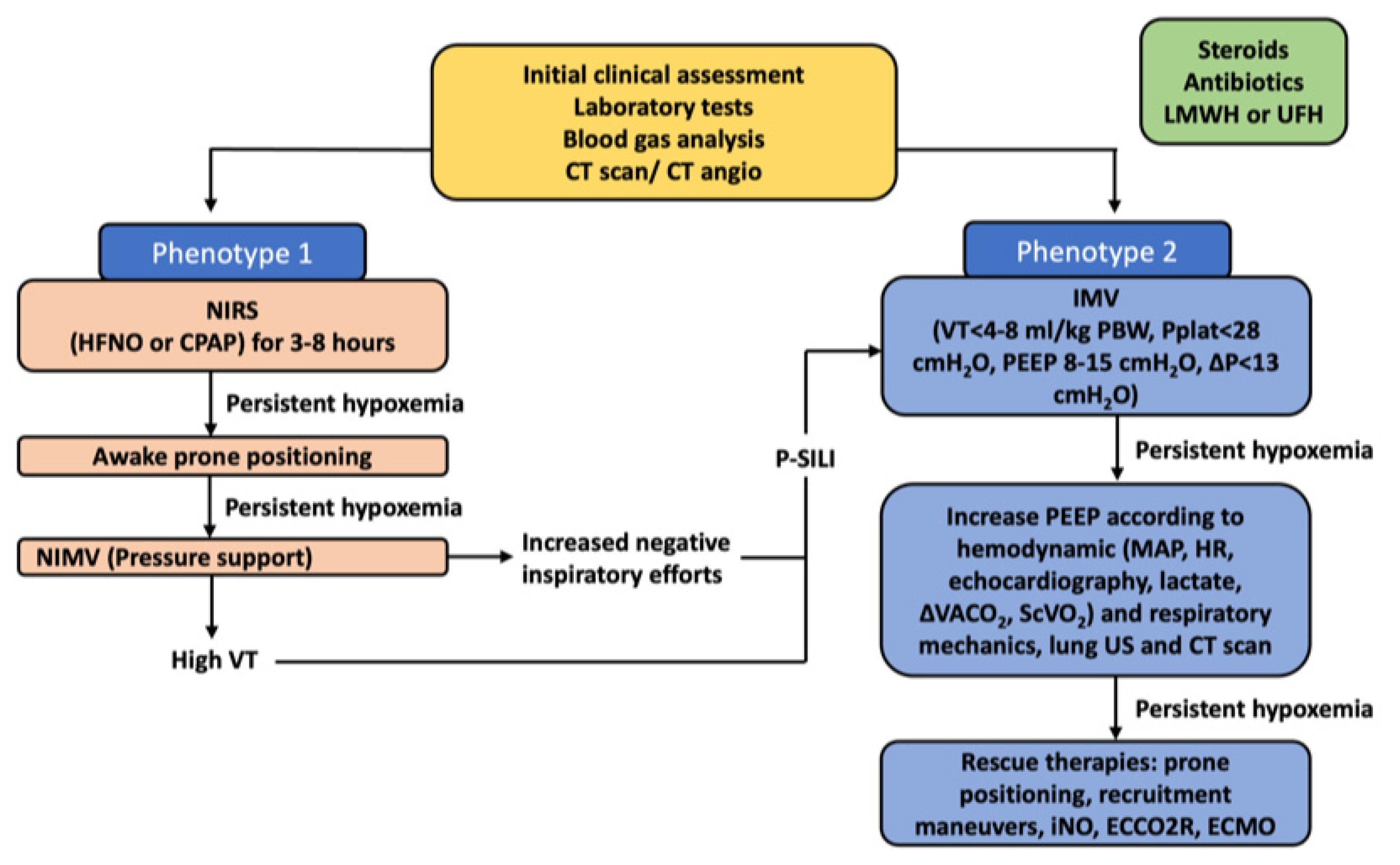
Jcm Free Full Text Different Methods To Improve The Monitoring Of Noninvasive Respiratory Support Of Patients With Severe Pneumonia Ards Due To Covid 19 An Update Html
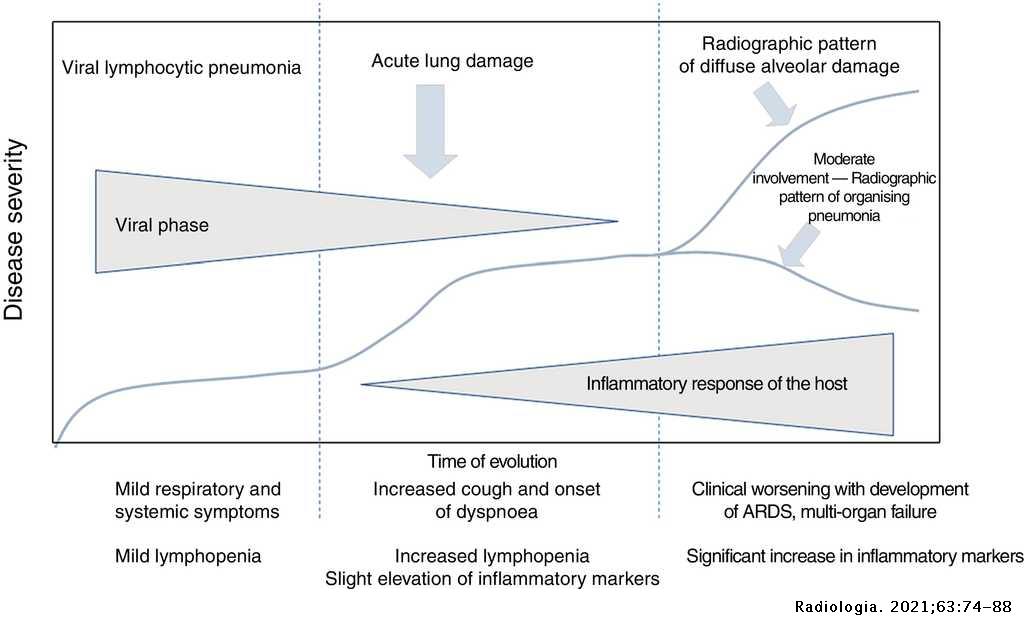
Radiologic Aspects Of Covid 19 Pneumonia Outcomes And Thoracic Complications Radiologia English Edition
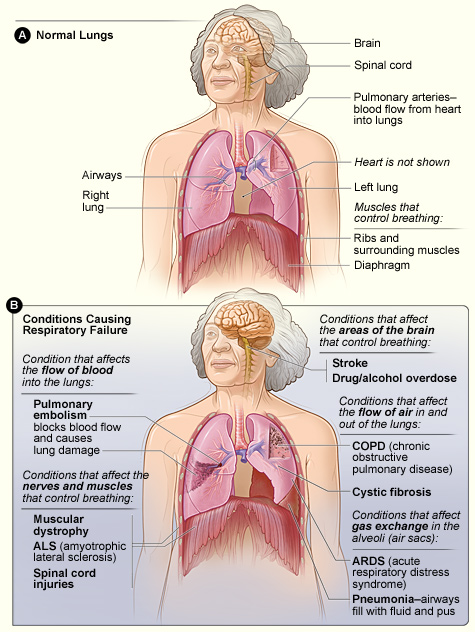
Respiratory Failure Physiopedia

Risk Of Acute Pulmonary Embolism In Covid 19 Pneumonia Compared To Community Acquired Pneumonia A Retrospective Case Control Study Clinical Radiology
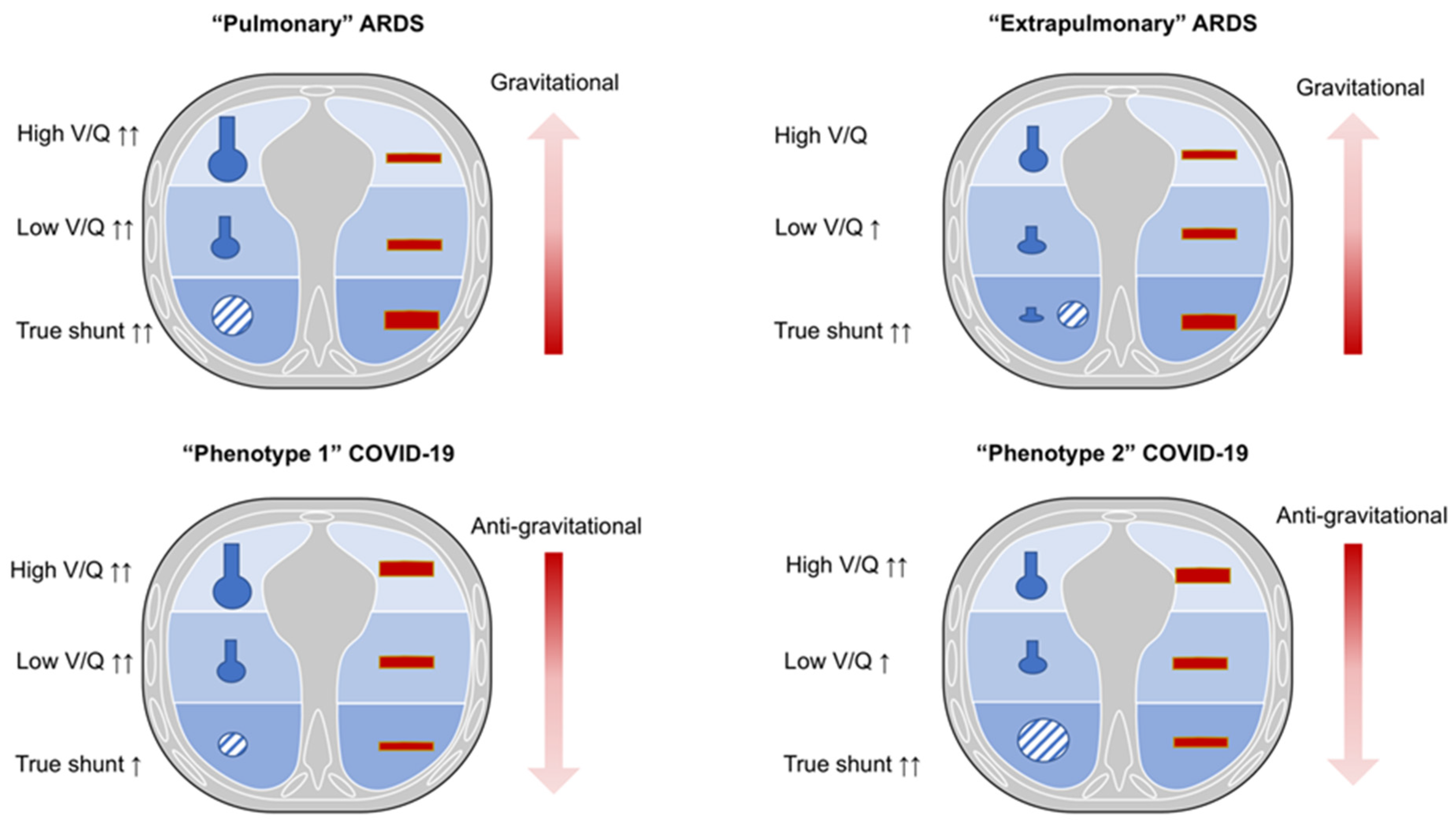
Jcm Free Full Text Different Methods To Improve The Monitoring Of Noninvasive Respiratory Support Of Patients With Severe Pneumonia Ards Due To Covid 19 An Update Html
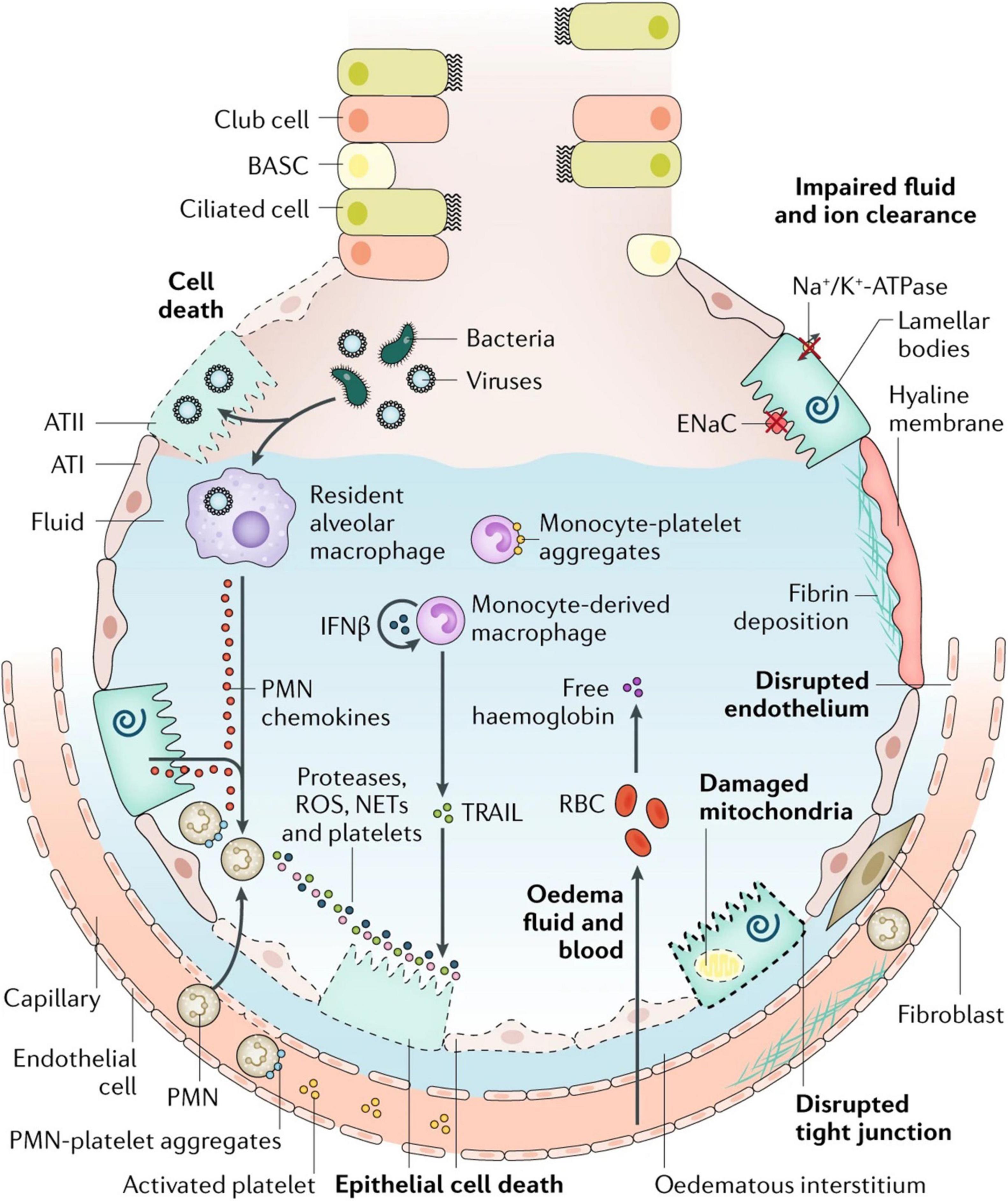
Frontiers Gene Therapy For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Physiology

Pulmonary Infarction In Acute Pulmonary Embolism Thrombosis Research

Reconsidering Ventilator Associated Pneumonia From A New Dimension Of The Lung Microbiome Ebiomedicine

The Prevalence Of Pulmonary Embolism In Patients With Covid 19 And Respiratory Decline A Three Setting Comparison Thrombosis Research

Mortality And Risk Factors Associated With Pulmonary Embolism In Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Scientific Reports

Hemoptysis Evaluation And Management American Family Physician

Dexamethasone Treatment For The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Local Modulation Of Antigen Presenting Cell Development After Resolution Of Pneumonia Induces Long Term Susceptibility To Secondary Infections Immunity

Comments
Post a Comment